Hydrangea ("hydrangea") is a flowering plant of the Hortense family. There are at least 52 species. Hydrangeas can be shrubs or creeping vines. They also occur in the form of small trees. Culture first came to Europe in the 14th century. The article offers to get acquainted with various representatives of the genus, learn to plant plants and provide proper care.
What is hydrangea?
Most often, Hydrangea is a bushy perennial flowering plant. Species are represented by both evergreen and deciduous specimens. In Russia, the latter are grown. In the natural environment, the species majority grows in East Asia, North and South America. The name comes from the Latin word hortus, meaning "garden".
Did you know? The sister of the Prince of the Roman Empire, Carl the Unbreakable, was called Hortense. This name was very popular.
The Japanese call the adzsai culture. Literally - "purple sunny flower." This naming is very justified - various shades of blue and red, all shades of purple vividly characterize some species. White inflorescences are also traditional.

Biological description
A spherical bush (up to 3 m), a small tree or a vine (climbing up to a height of 30 m along tree trunks) - hydrangeas are so different.
All types have common botanical characteristics that combine plants in one genus:
- flowering time - from spring to late autumn;
- types of inflorescences - panicle (up to 20 cm in diameter), scutellum;
- two types of flowers - small fruiting in the center and large sterile at the edges;
- the dependence of the shade on the level of soil acidity;
- fruits - boxes;
- leaves with an ovoid pointed shape, wide, saturated green;
- the root system is superficial.
Please note - the flowers of the culture, as a rule, have no aroma, their shape and size are attractive.
Plant characteristics
Plants are considered shade-loving.but they bloom only in the sun. Therefore, severe shading threatens that the flowering will not be of high quality and the shoots cannot develop normally.
The second feature of hydrangeas is the need for moist soil, which should be:
- fertile;
- sour;
- with the addition of peat.

The culture prefers the presence of mulch in the form of coniferous bark, peat or a pine needle. Winter-hardy are not all generic representatives. The strongest are panicle, tree-like, groundcover.
Important! It is useful to bring coniferous litter into the planting holes, this creates excellent conditions for the development of the measles system.
Types of Hydrangeas
Below, several species representatives of the family will be considered. They differ in the rules of care. Each of the species needs to be specially cut, some are very important to insulate for the winter. Of course, their external signs differ, for example, the color of inflorescences.
Large leaf
Hydrangea macrophylla - large-leaved hydrangea. It is grown not only in open-air gardens, but also in containers. Frost resistance of species representatives is low due to weak shoots. They are grassy in the first year of life. Buds of future flowers are laid on the branches in the autumn season.

The shape of the inflorescences is special - hemispherical, otherwise called umbrella or Japanese. Varieties are characterized by a noticeable effect of pH on the shade of the petals and sepals (blue, lilac, blue).
Did you know? Panicled hydrangea grows in the garden for a long time - up to 40 years.
Panicle
Hydrangea paniculata in the natural environment can reach five meters in height. Winter hardiness of the species is excellent, which is associated with the characteristic of shoots - they quickly wood. The flowering of species representatives is plentiful, the form of inflorescences is pyramidal. An amazing change occurs during the season with the color of the flowers: first pale green, then white. Soon they turn pink, and after that they get a brick tint.

Climbing, or petiolate
Hydrangea petiolaris is another interesting species. Petiole hydrangea is a vine - it is customary to attach it to tree trunks, walls. A plant that braids large boulders looks beautiful. It has aerial roots and suction cups.
Otherwise, the culture can develop as a bush form - up to 2 meters, it is also able to spread along the ground.
The peculiarity of the species is that flowering occurs only after a few years. Inflorescences consist of small and large flowers of white color. Amazing: this species representative has a smell! In landscape design, it is used as a decorative street creeper, decorating the space with its foliage.

Radiant
Hydrangea radiata grows naturally in the forests and mountainsides of North America. Frost tolerance of this culture is low, therefore, the cultivation of radiant hydrangea in Russia is difficult.
Characteristics:
- deciduous bush up to 2 m;
- shoots: pubescent;
- leaves: oval-lanceolate, their reverse side is pubescent, has a whitish hue;
- inflorescences: corymbose, up to 12 cm;
- flowers: white.

Tree-like
Species Hydrangea arborescens - large-sized shrub plant. Inflorescences in tree hydrangeas are formed on annual shoots. Initially, the hue of the flowers is greenish, over time it changes and becomes white.
Other features:
- inflorescence size - up to 15 cm;
- flowering - from July to October;
- not fully lignified branches freeze.

Dubolistnaya
Hydrangea quercifolia is vulnerable to colds. Dubrovolny hydrangea should be insulated for the winter. With proper care and protection from frost, the plant gives an excellent result - lush flowering. The peculiarity of the species is the presence of patterned leaves. The height of the culture is up to 2 m, inflorescences reach 30 cm in length, their shape is non-standard - elongated. Surprisingly, over time, the white color is replaced by purple.

Groundcover, or Himalayan
Hydrangea heteromalla - groundcover, ragged hydrangea. A plant reaching a height of three meters is convenient for standard use. The length of the leaves can be 20 cm. Their peculiarity is in the difference between the sides: the upper one is smooth and the lower one with pubescence, which is why the species is called.
And inflorescences of culture are non-standard:
- form - corymbose;
- color - from white to pink;
- flowering time - later (from late June or early July).

Serrate
One and a half meter representatives of the species Hydrangea serrata have rounded, almost flat inflorescences with wavy edges of the petals. Leaves are characterized by a serrated border. Serrated hydrangea is another owner of amazing shades during flowering - from lilac to blue. The flowers in the center are small, located at the edges - large, all of them are made up of a shield. Blue appears during growth in acidic soil, whiteness or greenishness is acquired upon development in neutral soil, and pink appears in alkaline soil. Coloring throughout the entire period is also variable.

Landing
Planting young shrubs is easy. It is important to remember the culture requirements for soil and light. The following is a description of planting instructions as a flowering decoration for your site.
Important! Do not plant cultivars near other plants that have a superficial root system. In this case, both of them will not be enough moisture.
Seat selection
Perennial prefers a well-moistened, drained place, the pH level of the soil is slightly acidic. It is especially important to remember this for varieties of large-leaved hydrangea, the flowers of which, with an increase in acidity relative to the norm, acquire a blue tint. Light shading will be justified, but it is important to plant a shrub in a place where it will bloom in the sun.

Landing time
There are two optimal dates: the first half of May and September. The soil must be warm. Do not plant hydrangea if there is a chance of sudden frost. Usually at the indicated time the weather favors landing.
Soil preparation
Instructions for the formation of landing holes is as follows:
- Dig indentations measuring 50 × 50 × 60 cm.
- Keep a distance of 1–1.5 m between the stands.
- Make a soil mixture: take 2 parts of humus and leaf soil and 1 part of sand and peat.
- Add fertilizers to this soil: for 10 kg of humus, 20 g of urea and potassium sulfate, as well as 60 g of superphosphate.
Landing process
The seedlings ready for planting should be placed in the recesses and filled with the prepared mixture so that the root neck is not below the ground. Then it is useful to slightly compact the earth. Then hydrangeas are watered, and the soil around them is loosened. It is important to protect young plants from the midday sun and open wind, mulch them with coniferous litter or a layer of peat and pine bark.

How to care
Several care activities will help maintain the normal development of shrubs in your area. Feeding, watering and pruning is described below. It is important not to forget about mulching the soil and supplying it with oxygen. But first, pay attention to the preparation for winter, because it should be done for varieties that do not have good frost resistance.
So, the rules for wintering hydrangeas:
- Paniculate spud with manure.
- Young bushes of even persistent tree-like varieties should be protected for the first two years so that the roots do not freeze.
- The winter mulch layer of peat and leaves is at least 15 cm.
Watering
Plants of this culture are hygrophilous. Regularity and irrigation rules:
- weekly irrigation;
- water volume - up to 20 l for each bush;
- during the rainy period you need to water less - up to 5 times a season.

Top dressing
When making the soil mixture described above during planting in the wells, it is not necessary to feed the crop for the first two years.
Did you know? Irrigating shrubs with a solution of aluminum alum at the rate of 40 g per 10 liters of water, you will achieve a change in the color of the flowers: white will turn blue, and pink will acquire a purple hue.
After this period, it is important to regularly fertilize:
- for the first time in early spring, complex mineral compositions are added (30 g per ten-liter bucket of water);
- you can use another method - add 20 g of urea, 35 g of superphosphate and the same amount of potassium sulfate to 1 m²;
- the second top dressing consists again of minerals, and is carried out during the budding period (up to 80 g of superphosphate and up to 50 g of potassium sulfate per 1 m²);
- the third time hydrangea is fertilized with mullein solution (1:10);
- also reapplied, with both last additives being added during the summer.

Mulching and loosening of soil
Often you do not need to loosen the soil, just do it a couple of times a season. Manipulation is performed after weeding and watering the plants to a depth of about 5 cm. Constant maintenance of mulch will not allow moisture to evaporate from the upper layers of the earth. It is customary to mulch with peat and sawdust so that the coating height is about 6 cm. If you create such a layer in the spring, then most likely it will not be necessary to update it until the fall.
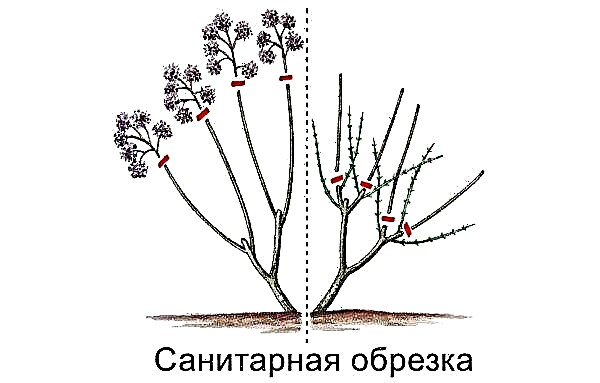
Plant pruning
The right month to trim - March. Cut shoots so that 6 to 12 of the strongest remain. It all depends on the age of hydrangea and the size of the bush. The remaining branches are shortened by several buds (up to five).
Further care is to remove all blooming inflorescences. As a rule, they do this in the fall. Radical pruning is performed only in relation to old bushes: you need to cut the stems, leaving stumps up to 8 cm tall. This method is not dangerous, but useful. In the next year, culture will give young new shoots and will bloom perfectly.

Breeding
You can increase the population of varietal specimens in all ways, even seed. But vegetative methods are successful: cuttings, propagation by layering and separation of the bush.
Seeds must be sown from April to May directly in the open ground. It is important to prepare the beds in advance, to add organic matter to them in the fall. Seedling care is long, complex, and young plants will bloom in the third year.
Important! All decorative varietal data disappears during seed propagation.
Can be sown in pots without deepening the seeds. It is important to maintain humidity and cover the container. In 20 days, seedlings will appear, they are looked after for two years, and for the third - they are planted in a permanent place of cultivation.

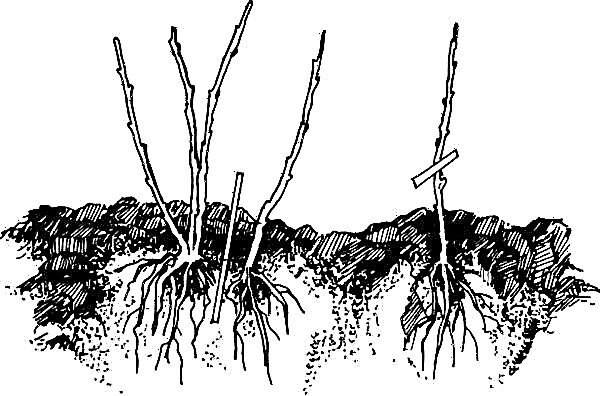
Bush division - a simple option. It is necessary to water abundantly in early spring, carefully dig up the culture, divide it into separate parts and plant it according to the planting agricultural technique. Dividens take root during the summer period. Tip: it’s useful to cut the ends of the shoots and roots!

Cuttings should be taken from annual branches during pruning. They do this later, in June or July. It is definitely worth removing the upper part with the bud from the trim. After that, it is useful to treat the material with a growth stimulator. Then deepen the planting material into the mixture of peat and sand by 3 cm. It’s easy to care for - spray with a spray bottle, cover with a film. It takes about 25 days to root. After - you can plant sprouts that take root well before the winter.
Layering in early spring, you need to bend to the soil, slightly cutting the bark and sprinkling with soil. It is important to strengthen the shoots. Then they should periodically be spudded. Each stalk will give several branches, which in October can be dug up and divided. But it is better to leave them until next year.
A beautiful plant is popular in America, Europe, in the East. Domestic gardeners and summer residents love it very much. Large inflorescences of rare shades are in harmony with greenery and undersized herbs and shrubs. In landscape design, hydrangea is "respected" for its long life, the size of the flowering part, and the variety of foliage. Decorative varieties of winter-hardy species in the middle lane and in the suburbs are actively grown and propagated. They are so attractive that they are very active in garden centers, nurseries and shops. On the Internet you can find product catalogs at low prices on specialized sites, and select the desired hydrangea for home delivery.