Often, gardeners complain that spots and areas covered with gray fluffy mold appear on the cucumber plantings. This is botrytis or gray rot, a very dangerous fungal disease to which vegetables are susceptible. This article is devoted to the fight against gray rot on cucumbers, here we will give possible ways to combat chemical and biological drugs with this disease.
What is gray rot?
Botrytis cinerea - a mushroom whose spores are a distributor of gray mold on cucumbers and other vegetable crops.  Botrytis cinerea In addition to cucumbers, gray mold is also affected: peppers, lettuce, beans, cabbage, onions and tomatoes. Especially often, the disease affects plants in greenhouses and greenhouses in winter and early spring, when air temperature and humidity are quite high, and ventilation is limited.
Botrytis cinerea In addition to cucumbers, gray mold is also affected: peppers, lettuce, beans, cabbage, onions and tomatoes. Especially often, the disease affects plants in greenhouses and greenhouses in winter and early spring, when air temperature and humidity are quite high, and ventilation is limited.
The main symptoms of botrytis are gray fluffy plaque and brown spots on the stems and leaves. The infected flowers and ovary become brown and die, and the fruits begin to rot. Even if it was possible to avoid external signs of botritis development before harvesting, it is possible that gray mold can destroy cucumbers during transport or storage.

Gray mold affects the stems of plants near the ground and causes rotting in the aerial part of the shoot. Brown and dead spots are formed on the plants, and the cucumber fruits infected with the disease acquire gray, watery, round spots, from which rot begins.
Also from the diseased bushes the fruits fall prematurely. In places of damage, a gray or brown fluffy coating appears, this is the mycelium, from which, after maturation, spores of gray mold stand out. The infected plant dies quickly.
Did you know? There are specially bred varieties of cucumbers, in which a tiny size is genetically laid, their fruits are used to pickle capers. Up to 25 can fit in a 500 ml jar–30 tiny cucumbers.
The development of botritis, in addition to high humidity and limited ventilation, contributes to a lack of lighting, as well as weakening of cucumbers by other diseases or excessive compaction during planting.
Video: gray rot on cucumbers
The main reasons for the appearance
Gray mold develops quickly on cucumber beds as soon as the growing conditions become optimal for the development of fungal spores.
This happens if the temperature conditions are not observed during the growing season of the cucumber, the plants are irrigated and irrigated, the crop is grown without crop rotation, the wrong (too dense) scheme for growing the cucumber is applied, there is no airing and other deviations from the agricultural technology of this crop are practiced.
Temperature violation
Fluctuations in temperature from high to low, usually poorly affect the health of cucumbers. The sharp differences in day and night temperatures become the reason for a significant decrease in plant immunity. On weakened plants, spores of fungi quickly begin to develop.
The optimum temperatures at which cucumbers remain healthy vary in the range +22 ... + 28 ° C during the day and in the range +18 ... + 22 ° C at night. Overheating is considered to be daytime temperature above + 30 ° C and nighttime temperature below +23 ... + 24 ° C, which provokes accelerated aging of cucumber bushes.
If the temperature in the street or in the greenhouse, depending on the method of cultivation, drops to + 8 ° C or lower and holds for at least 24 hours, then irreversible changes occur in the development of cucumbers, leading to the death of the plant, disease or low yield .
Wrong watering
In no case should cucumbers be watered on a leaf (by sprinkling), since drops of moisture on the leaves remaining for several hours contribute to the activation of fungal spores, which until then have been latent.
Cucumbers are watered only under the root, trying not to moisten the stem or leaves during irrigation. When growing cucumbers on street beds, in the root zone of plants create a soil recess (aryk) for irrigation.

In greenhouses and hotbeds, drip irrigation is often used. The drip irrigation system is cheap, with careful use and folding at the end of the summer season, it lasts for three to four years.
Drop watering is good because the gardener can calculate the exact amount of moisture that gets to each plant. Also, drip irrigation can be applied to liquid fertilizers, combining them with irrigation.
Did you know? Interesting cucumber varieties were brought from China to Russia (Chinese Miracle, Chinese White), the fruits of which have a length exceeding 100 cm. When grown on a trellis, the fruits of such varieties hang down, under the gravity, like straight, outlandish batons, and when grown on the bed "in the open" cucumbers curiously curl or curl up.
Affection for one place
Cucumber culture is very dependent on crop rotation. You can’t grow cucumbers for cucumbers for several years in a row. This not only leads to soil depletion, but also accumulates the pathogens of diseases of this culture in the same place, which increases the risk of developing diseases on cucumbers in the next season.
It is recommended as a predecessor of a cucumber to grow any kind of cabbage on the garden. Also, tomatoes, potatoes and other members of the solanaceous family are suitable as a predecessor culture.

Unregulated Humidity
Lack of watering and excessive moisture in the soil are dangerous for cucumber plantings. When growing cucumber seedlings, air humidity is maintained in the range of 70–75%; for adult plants, air humidity is permissible in the range of 85–95%.
Also, the gardener should pay attention to soil moisture. Before the crop blooms, the soil under the plants should have moderate humidity, and when the flowering period begins, the humidity rises to 80%.
Excess fertilizer
The culture of cucumbers is very fond of nitrogen fertilizers, such as fresh manure of cattle, humus or compost. But the gardener needs to remember that an excess of nitrogen under the cucumbers leads to an outbreak of fungal diseases and the development of rot on the roots and fruits of plants. With other varieties of top dressing, you must also be careful not to overfeed the plants.

Cucumbers feed four times over the entire growing season:
- the first top dressing is carried out 2 weeks after transplanting;
- the second top dressing is introduced at the beginning of the flowering period;
- fertilizing a third time is necessary in the middle of the fruiting period;
- the fourth top dressing is done 45–55 days after transplanting seedlings in the garden.
Lack of ventilation
With greenhouse cultivation, a gardener can not do without systematic ventilation. During the ventilation of the greenhouse, air humidity decreases, therefore this procedure is necessary to avoid the development of fungi on the plantings.

In the early spring, the greenhouse is aired twice a day. The airing time does not exceed 10-15 minutes, since the air in the street at this time is still cold, and the plant grower should not greatly cool the air in the greenhouse. When ventilating the greenhouse, the gardener should open the windows only on one side of the structure.
Important! The gardener should remember that cucumbers grown in the greenhouse, unlike tomatoes, do not tolerate drafts. This difference between the two popular greenhouse crops does not allow them to be grown together in the same greenhouse.
Tightness
When planting seedlings or sowing cucumber seeds in the ground, it is necessary to observe the scheme for growing the crop and not exceed the recommended distance between the cucumbers in the rows and between the plants.
It is optimal to grow this crop according to one of the schemes:
- Scheme No. 1 of vertical cultivation (on a trellis) - plants are arranged in one row, observing the interval between rows of at least 120–150 cm. The distance between the bushes of cucumbers is 10–15 cm.

- Scheme No. 2 of vertical cultivation - cucumbers have two rows parallel to each other, observing the interval between rows of 80-100 mm. The gap to the location of the next two rows of vegetables should be at least 150 cm. With this scheme, keep a distance between cucumber bushes of 20–25 cm.
 This scheme of cultivation implies that all plants in one row are slightly biased with respect to the arrangement of cucumbers in a parallel row, that is, a “checkerboard” arrangement is observed. Offset plantings allow plants to give 50% more lighting, in addition, the bushes will be ventilated without interference, which will additionally protect the cucumbers from the development of gray rot.
This scheme of cultivation implies that all plants in one row are slightly biased with respect to the arrangement of cucumbers in a parallel row, that is, a “checkerboard” arrangement is observed. Offset plantings allow plants to give 50% more lighting, in addition, the bushes will be ventilated without interference, which will additionally protect the cucumbers from the development of gray rot.
Important! When growing greenhouse cucumbers in thickened plantings, in conditions of high humidity and unstable temperature, cucumbers quickly become ill. This is because it is not possible to dry the surface of plants from moisture droplets that have settled on their surface.
Disinfecting disinfection
At the end of the growing season, the gardener needs to disinfect the soil in the greenhouse. Disinfection is also carried out on street beds, especially if, during growing, cucumbers fell ill with one of the fungal and bacterial diseases.
After the autumn harvesting of the greenhouse from plant debris, all surfaces and soil are treated. For this, a fungicide solution is used, it is applied by fine spraying with a garden sprayer.

General rules for processing cucumbers
Both biological and chemical treatments of cucumber plantations are necessarily carried out in the morning. Compliance with this condition is extremely important, since during spraying a moist solution is applied to the stems and leaves of the plants, which must dry before evening.
If this condition is not met, then activation of fungal spores may occur during wet nights overnight. If the processing of plantings is carried out in a greenhouse, then to speed up the drying of the vegetation from moisture, several times a day the room is aired.
If the processing of cucumbers is supposed to be carried out on a bed located in the open air, in addition to the morning time, you should choose a dry, sunny day for work. If it rains within 3-4 hours after the chemical or biological treatment of the cucumber plantations, the event will have to be repeated the next day, after the plants have dried after rain.
Important! All work on processing plants with chemicals should be carried out by a person dressed in overalls, consisting of: trousers and a shirt with long sleeves, a hat, glasses, boots and a respirator. After carrying out work, overalls should be washed, parts of equipment that cannot be washed should be well washed under running water, it is recommended that a person take a shower.
Folk remedies
Gardeners have many recipes for protecting cucumber bushes from rot and other diseases caused by fungal spores. All folk remedies are effective, mainly as preventative measures.
Folk ways to combat gray rot:
- Wet soil in a greenhouse under cucumbers is dusted with wood ash sifted through a fine sieve. This tool prevents the occurrence of basal and gray rot. Also, ash can be applied to the leaves and stalk of the cucumber, in addition to protection against fungal spores, this will serve as an additional foliar feeding of plantations.

- Cucumber plantings are treated with a solution of water and fermented milk products such as kefir, sour milk or whey. To make a working solution, add 1 liter of dairy products to 10 liters of water and mix thoroughly.
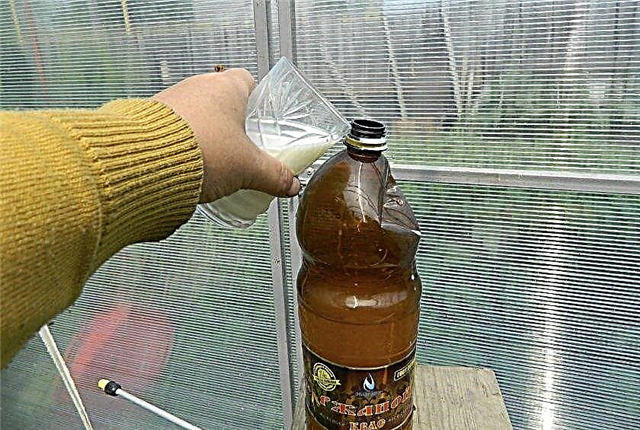 For applying the finished solution to the planting, use a conventional broom. A broom is dipped in a bucket of solution and the medicinal fluid is sprayed on the plants. The procedure is carried out regularly, every 2 weeks, until the end of the fruiting of the culture.
For applying the finished solution to the planting, use a conventional broom. A broom is dipped in a bucket of solution and the medicinal fluid is sprayed on the plants. The procedure is carried out regularly, every 2 weeks, until the end of the fruiting of the culture.
Biological products
Some gardeners, in order to obtain a biologically pure crop of fruits, avoid chemical treatments. Instead, they use biological antifungal drugs to prevent gray rot and to treat already sick cucumbers.
Modern industry offers drugs: Fitodoctor, Trichodermin, Fitoverm, Guapsin, Fitosporin-M. These plant protection products do not contain chemistry and are organic.

No matter how tempting the idea of growing organically pure cucumbers is, gardeners need to carefully monitor the condition of the plantings, since biological products may not cope with the task of protection. Especially if the period of plant infection has already begun and is in the stage of active development.
Chemicals
To protect cucumbers from fungal diseases, in particular from gray rot, gardeners use fungicides containing active elements to combat fungal spores and bacteria. Fungicides are used both as preventive measures and for the treatment of plantings already affected by the disease.
Effective drugs for the treatment and prevention of gray rot:
- Topsin-M 500 SK - one of the most effective fungicides. The product contains methyl thiophanate (500 g). In addition to the fight against gray mold, the drug is used to combat verticillosis. Plants are sprayed immediately after the first symptoms of the disease are detected. The procedure is carried out only once per season at a dose of 150 ml of the product per 100 liters of water.

- "Prolectus 50 WG" Is a fungicide containing the active substance fenpirazamine (pyrazole compound - 500 g / kg). The drug has a deep and contact effect, it is used for the prevention and control of fungal diseases of vegetable plants (cucumbers, tomatoes, eggplants, peppers, zucchini and other pumpkin crops). Processing with this drug is carried out as soon as the first symptoms of the disease appear. The drug is diluted in a dose: 80-120 g of the product per 100 liters of water.

- Signum 33 WG - it is a systemic fungicide in the form of granules, the drug is intended for prophylactic and medicinal use. It contains boscalid (26%) and pyraclostrobin (6%). The drug is used in an amount of 0.75–1 kg / ha to combat gray mold on cucumbers and cabbage.
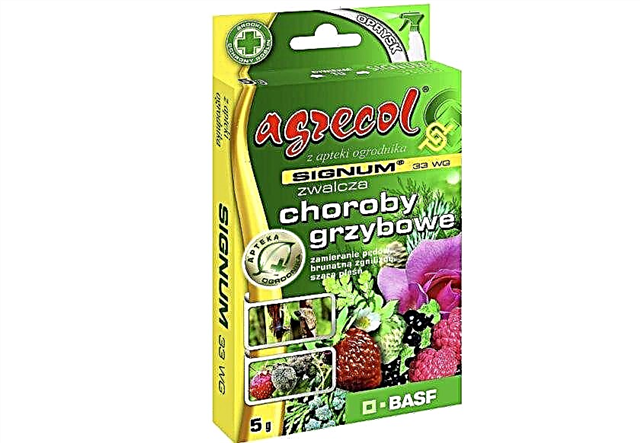

- "Switch 62.5 WG" - fungicide with a deep and contact action, intended for the prevention and treatment of cucumbers from fungal diseases. For the season, two treatments are carried out with an interval of 7 days. The active ingredients of Switch 62.5 WG are cyprodinil - 375 g, fludioxonil - 250 g. The preparation has a very short waiting period for harvest after processing, only 3 days when growing cucumbers, tomatoes, zucchini, pepper. When processing cucumbers, the drug is used in an amount of 0.75–1 kg / ha.

Maintenance work from gray rot
In order to prevent the occurrence of gray rot on the plantings of vegetable crops, it is necessary to carefully collect the remaining vegetation remaining after harvesting. Pathogens of fungal and bacterial diseases can winter on organic residues.
The collected plant debris can be buried in the soil, but they must be buried so that a layer of soil at least 50 cm thick is laid on top.If the burial depth is insufficient, during spring digging or plowing, the pathogens will again appear on the surface of the bed.
Did you know? More than 95% cucumber pulp consists of water. That is why a couple eaten in the morning, after a fun alcoholic party, cucumbers, can save a person from headaches and hangovers.
It would be much more reliable to wait until the remains in the garden dry well in the fall, collect them in a pile with a rake and burn them. Fire reliably cleans the garden of pathogenic pathogens. At the end of the greenhouse season, it is necessary to disinfect all greenhouse equipment and garden tools. To do this, tools washed from the soil are soaked in a solution of water and bleach.
A disinfectant solution can be made using inexpensive household chemicals for processing home plumbing, for example, "White". To prepare a solution in 500 g of pure water, 500 ml of White is diluted. Soaking time of garden and garden tools 20-30 minutes.
Greenhouse equipment, such as seedling pallets, pegs or pots, are also soaked in this solution. The cords that served in the summer for the vertical garter of cucumber bushes in autumn must be taken out of the site or burned, since pathogens of gray rot can be located on them.
Botritis or gray rot, a very dangerous disease for plants, having a fungal nature, so it is very difficult for gardeners to protect plantings from fungal spores. In order to prevent the occurrence of the disease, the plant grower needs to take preventive protection measures on cucumber plantations, it will be simpler and easier than treating diseased plantings.


 This scheme of cultivation implies that all plants in one row are slightly biased with respect to the arrangement of cucumbers in a parallel row, that is, a “checkerboard” arrangement is observed. Offset plantings allow plants to give 50% more lighting, in addition, the bushes will be ventilated without interference, which will additionally protect the cucumbers from the development of gray rot.
This scheme of cultivation implies that all plants in one row are slightly biased with respect to the arrangement of cucumbers in a parallel row, that is, a “checkerboard” arrangement is observed. Offset plantings allow plants to give 50% more lighting, in addition, the bushes will be ventilated without interference, which will additionally protect the cucumbers from the development of gray rot.
 For applying the finished solution to the planting, use a conventional broom. A broom is dipped in a bucket of solution and the medicinal fluid is sprayed on the plants. The procedure is carried out regularly, every 2 weeks, until the end of the fruiting of the culture.
For applying the finished solution to the planting, use a conventional broom. A broom is dipped in a bucket of solution and the medicinal fluid is sprayed on the plants. The procedure is carried out regularly, every 2 weeks, until the end of the fruiting of the culture.