Mid-season Barin potatoes are one of the promising young varieties registered in the State Register of the Russian Federation in 2014. Selection work was carried out under the leadership of the All-Russian Research Institute of Potato Farm named after Lorch with the participation of more than 10 other companies. More information about the variety and the features of its cultivation - in this review.
Description and characteristic
The variety was obtained relatively recently, so it did not have time to become widely known. Zoned for winter hardiness zone 4 (USDA) with a minimum winter temperature of -35 ° C, but can also be grown well on a personal farm or on an industrial scale and in the middle zone of Russia.
We can assume that Barin is a slightly modified version of the Baron variety from which it comes. The difference between the two varieties is that Barin ripens a little later and is not intended for cultivation in the northern regions. Among its advantages: unpretentiousness and undemanding to growing conditions.
Did you know? Indigenous peoples of America began to grow potatoes as early as 8000 BC. e. But Europeans met him only in the era of the great geographical discoveries.
The bushes of Barin are characterized by an average growth force. The height of the stems is about 50 cm. The leaves are medium sized, emerald green with waviness along the edge of the leaf plate. Potato blooms with large purple-pink flowers at the top of the bush.
The variety is distinguished by medium-sized tubers. Their weight is about 80–120 g. Such a weight of tubers is convenient for catering enterprises: it is portioned and it is easy to clean it mechanically.
Tuber Characteristic:
- peel color: beige;
- texture: smooth, thin;
- flesh: light yellow, dense;
- eyes: small;
- starchiness: 13-15%.

Taste qualities
Barin has excellent taste characteristics and presentation of tubers. Tender and starchy potatoes go well with butter, cheese, sour cream. It is a source of vitamins C and B6, fiber, manganese, phosphorus and other nutrients. The sweet taste of potatoes provides a high content of carotenoids.
Ripening period
Barin's originators position him as a mid-season table variety. You can dig up young potatoes already on the 50th day after the emergence of seedlings. And for the full ripening of the crop, it will take 70–75 days.
Productivity
One bush, Barina, will provide you with 8-12 oval-shaped potatoes. The declared yield of the variety is 280-300 kg / 100 m². Yields are affected by soil fertility and the quality of planting material.

Disease resistance
The originator declared the resistance of the variety to cancer and the presence of susceptibility to the golden nematode. Growing potatoes of any kind on swampy, moist soil is likely to cause infection by rot or bacterial diseases, which is why crop conditions are greatly affected by the conditions in which the potatoes are grown.
Important! Varieties of potatoes with a light skin are stored less than with red, so eat Barin tubers in the first place.
Advantages and disadvantages of the variety
- Advantages of the Varin variety:
- unpretentiousness;
- resistance to weather conditions;
- good keeping quality;
- stable yield;
- uniform, easy to clean tubers;
- excellent taste and starchiness;
- cancer resistance.
- Potato disadvantages:
- zoned only for the central regions of Russia, therefore, there is no data on yield in other regions;
- most likely, viral or bacterial infections affect it in the same way as any other potato, since its originator does not indicate its resistance to these diseases.
Planting and growing varieties
Agricultural cultivation of varieties is considered standard. It does not require special care or unique fertilizer systems to produce high yields. Like other plants that form tubers, potatoes need fertile soil with a loose structure, although it can grow on most types of soils.

To get a higher yield, potatoes need:
- regular top dressing;
- weekly watering;
- loosening;
- hilling;
- weed removal;
- pest and disease control measures.
For planting, choose a sunny area in which the sun is at least 6 hours a day. It must be drained. If the soil is poor in nutrients, then fertilizers must be applied.
The timing
Variety Barin tolerates cool weather. It can easily tolerate short-term frosts, so it can be planted in early spring at an air temperature within +7 ... + 13 ° C. Soil temperature should not be lower than 0 ° С.
Important! It is believed that the optimal landing time, which gives the best result, — for 2–3 weeks before the last soil freeze.
At sub-zero temperatures, potatoes will not develop. In addition, tubers can be affected by soil microorganisms while they are in moist and cool soil. You can continue to plant tubers until mid-April.
Crop rotation rules
Crop rotation is required due to the fact that one and the same crop or a diet similar to it depletes nutrient reserves and promotes the propagation of pests. For convenience, plants are divided into 4 groups according to a similar type of nutrient intake and the same pests.
It:
- legumes;
- root crops, tubers and bulbs;
- leafy greens (spinach, lettuce, cabbage);
- fruit-bearing (tomatoes, cucumbers, peppers, eggplant, pumpkin, melon, sweet corn).

That is why most schemes suggest that the site is necessarily divided into 4 sectors, in each of which crops of one group are planted. The next year they are changed, moving in a circle. In this case, potato precursors may be leaf crops or legumes.
It is forbidden to plant potatoes after potatoes or root crops. It is undesirable to plant after tomatoes, eggplant or peppers, but acceptable after cucumbers. Owners of household plots may not be suitable for such a system of division into sectors. Then they recommend alternating potatoes with siderat plants: legumes, alfalfa, and cereals.
They land in the summer after the main crop is harvested from the site. Their roots loosen the soil and accumulate nutrients. During the autumn digging of the site, they will be immersed in the ground and become fertilizers for spring crops.
Soil requirements
Clay soils must be plowed before planting potatoes to provide them with loose soil. When digging, stones, branches and other solid objects that can deform growing potatoes are also removed.

Basic soil requirements:
- good drainage;
- medium density (clay soil is diluted with sand, while sandy soil, on the contrary, is weighted with clay);
- good breathability;
- the acidity level is 5.5–7 pH.
Did you know? The largest crop from a single potato bush was obtained by the English farmer Eric Jenkinson in 1974. He amounted to 167 kg.
Preparing tubers for planting
Planting potatoes usually begins with the preparation of seed material. For this, small tubers are selected. Each of them should have at least 4 eyes. Each peephole will give 1 stalk. The more of them, the more powerful the bush and the better the crop.
Large potatoes can be cut, dried on the windowsill for 2–3 days, and treated with cut ashes to prevent infection with fungal spores or bacteria. Prepare planting material in February.

In winter, potatoes are at rest. Before planting, they must be germinated. This allows you to accelerate the growing season and reduce the ripening time of the crop. Germination period is 2-3 weeks.
The temperature in the germination room should be around + 14 ° C. If it is lower, just place the potatoes in a plastic bag. If above - find another room, otherwise the sprouts will stretch and weakened stems will result.
Landing technology
There are many methods for planting potatoes.
Consider the most popular of them:
- Most common method - "on the shovel". Wells with a distance between them of 30–40 cm are made on the site. Depth is 10 cm. Rotten manure or compost is laid on the bottom of the hole, then a small layer of soil. Potatoes are laid on it and covered with soil. As the stems increase, the bush grows up - they throw soil on it. This contributes to better tuber formation.
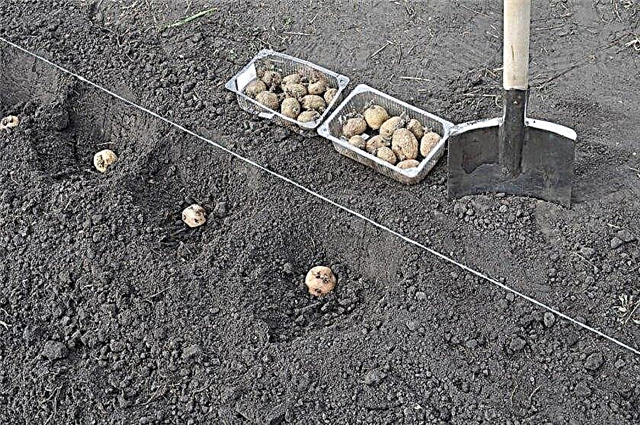

- In large fields use trench landing method. The depth of the trenches is 30 cm, the distance between them is 50–70 cm. Inside the trench, a kind of “layer cake” is obtained: first a layer of straw is laid, then a layer of organic fertilizers, then ash and a layer of soil. Potatoes are laid on this construction at a distance of 30 cm from each other and covered with a trench with soil.

- The straw method involves laying out tubers on straw. Then they are covered with a layer of the next straw 7–10 cm high. When the sprouts rise above the straw, they are covered with the next layer. The final height of the structure is 30–40 cm. The advantage of this method is that the straw retains moisture, prevents the tubers from contacting pests and weed growth. Harvesting is also very simple. There are also disadvantages: you may not have that much straw; moreover, mice also like to settle in straw.

- Seed potatoes are grown in special crates, car tires, and even in trash bags. But, of course, such methods cannot be considered as the main ones for planting large lots of potatoes.
Care Features
As soon as the sprouts appear, it is necessary to maintain a constant soil moisture. So that the moisture does not go away too quickly, the surface of the crops is covered with mulching material. It can be sawdust, straw, spruce branches, other materials. The layer thickness is at least 5 cm. Regular watering is also carried out, fertilizers are periodically applied and other measures are taken.
Fertilizer
Ideally, before applying fertilizer, you need to check the soil to know exactly how many and what elements it contains. A good test kit will allow you to measure the level of acidity, as well as the main nutrients: nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium.

Without analysis, you should look at the plants around. The abundance of weeds indicates acidification of the soil. Poor plants are evidence of a lack of nutrients.
Many farmers apply manure in the fall before spring planting of tubers. This is good, but the melting snow will wash off nitrogen from the manure introduced in this way, so it would be better if in the autumn you put lime to deoxidize the soil, and fertilizer - when planting potatoes. You will need 20 kg of rotted manure and 250 g of wood ash per 1 m² of soil.
Wood ash is also able to deoxidize the soil, so if you did not apply lime in the fall, then partially the level of acidity can change the ash. When using inorganic fertilizers, use formulations balanced as 2: 2: 3 (nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium). Read the application rate on the packaging. It will be approximately 200 g / 1 m². During the growing season, fertilizer application is repeated every 3 weeks.
Did you know? Potato leaves contain many carotenoids. It is thanks to them that the Colorado potato beetle acquires its bright orange color.
Watering
Potatoes are watered 2-3 times a week. Tie watering not to the number of times, but to how dry the soil is: if it is 5-7 cm, then it is time to water. If you meet unevenly developed tubers - this is the result of irregular watering. If potatoes experience periods of drought and heavy watering, they will develop unevenly.
Watering Rules:
- do not pour water on the bush, try to irrigate the root zone;
- water in the morning to limit contact of potatoes with plenty of moisture.

Weeding and hilling
Hilling is the increase in the amount of soil around stems in the shape of a hill. Tubers are thickenings on the roots. To have more of them, you need to increase the area on which they are formed, i.e., the root system. For this, they carry out the hilling.
When the sprouts reach a height of 10-15 cm, carry out the first hilling. The second is performed during flowering. At this point, the tubers are developing rapidly, and this must be done. For the Barin variety, 2 hills are sufficient, and for later varieties, 2-3 hills are performed.

The process must be combined with loosening and removing weeds. The depth of tillage is 4–5 cm. It is convenient to loosen the soil after wetting: watering or rain.
Loosening tasks:
- root system aeration;
- weakening the soil in order to provide tubers with better conditions for growth;
- weed control.
Important! Evening earthing up of potatoes is convenient because the leaves on the stems will be directed upwards and will not be accidentally covered with earth.
Prevention of diseases and pests of the variety
Potato diseases can be fungal, bacterial or viral in nature. They appear stains, rot and neoplasms on plant tissues. And bushes become infected through damage to leaves or roots by pests.
Among the main fungal diseases are late blight, black scab, alternariosis, powdery mildew, fusarium wilt. Bacterial nature - in ring rot, blackleg, bacterial wilt. Viral - mosaic, tuber necrosis, etc.
The main fungal diseases and their treatment:
- Late blight - A disease that occurs in early summer. It manifests itself as dark brown spots on the leaves. Later they completely dry out. Since this is a fungus, it is dangerous because of the possibility of infection of tubers.
 Pour spring beds with Ridomil solution. This is a highly active fungicide that completely destroys pathogenic fungi both in the soil and on plants. It is important to remember that drugs of this class are used only for treatment, and not as a prophylactic. It will be better if you process the planting material with Zircon before planting. This drug protects the tubers from fungi, and also stimulates their growth and development. For potatoes, you need 20 drops per 1 liter of water. Against diseases of a fungal nature, crops are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux liquid (1%). It is advisable to do this even before you detect signs of the disease - before hilling.
Pour spring beds with Ridomil solution. This is a highly active fungicide that completely destroys pathogenic fungi both in the soil and on plants. It is important to remember that drugs of this class are used only for treatment, and not as a prophylactic. It will be better if you process the planting material with Zircon before planting. This drug protects the tubers from fungi, and also stimulates their growth and development. For potatoes, you need 20 drops per 1 liter of water. Against diseases of a fungal nature, crops are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux liquid (1%). It is advisable to do this even before you detect signs of the disease - before hilling.Important! When spraying potatoes, pay attention to how many days it can be eaten. This information is necessarily available on the package with the drug.
- Black scab - appears as black dots on the tubers. This can be revealed even at the stage of preparation of planting material. Affected bushes are characterized by low growth, white coating on the stems and the presence of dry rot on them. Against the causative agent of the disease, the Quadrice soil treatment is mandatory.

- Alternariosis - manifested by dry spots on leaves that look like concentric annual rings on trees. If symptoms of the disease are detected, use "Poliram", "Profit".
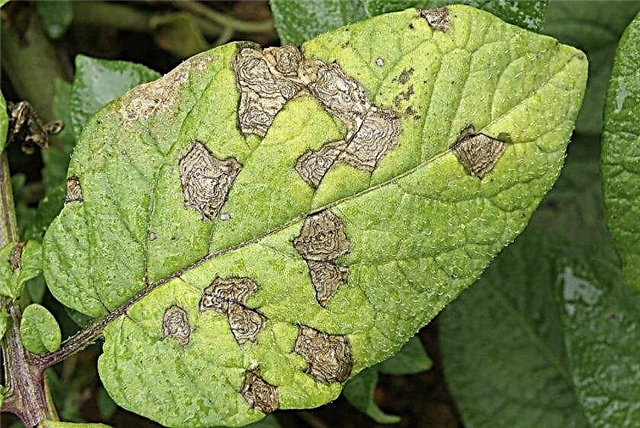

- Fusarium wilt - manifests itself in the form of yellowing of the leaf along the central vein. The sheet curls and fades. Preventively crops are treated with copper-based fungicides.

- Powdery mildew - similar to spots of flour on the leaves. When the first signs appear, they are treated with Bayleton or Tiovit.
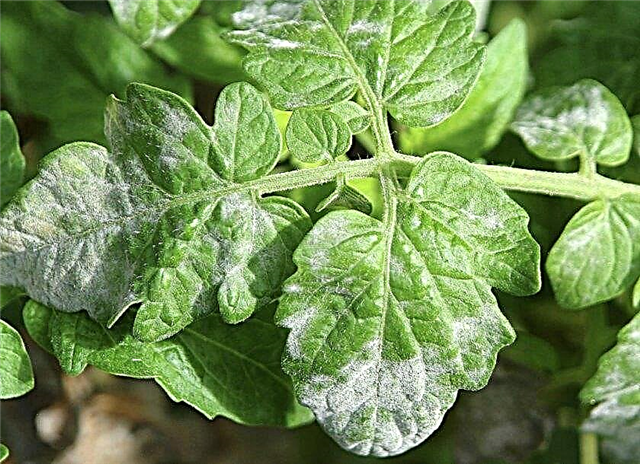

Diseases of a bacterial nature are not treatable. Diseased plants are dug up and burned away from the site. Of bacterial diseases, the Barin variety is resistant only to bacterial cancer.
Bacterial Potato Diseases:
- Ring rot - Visible only if the tuber is cut. This is a circle of small black dots that runs throughout the potato at a distance of about 1 cm from the surface.
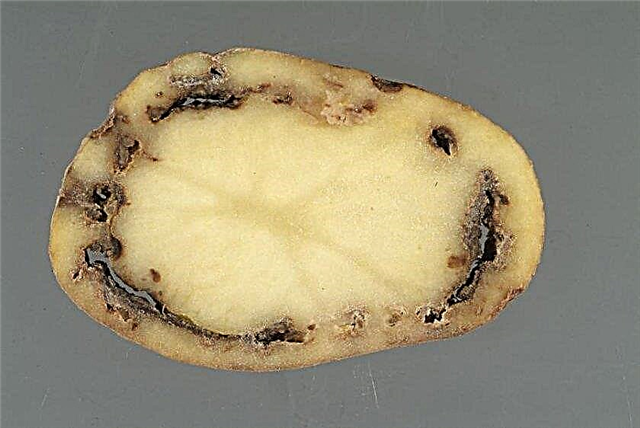 It is detected at the stage of preparation of planting material. After 20 days, black pits appear on such tubers.
It is detected at the stage of preparation of planting material. After 20 days, black pits appear on such tubers. - Blackleg - activated after rains. It affects the stems that blacken from below. The main means of prevention is the introduction of dolomite flour into the soil or its treatment with Bactofit.

- Bacterial wilt - begins with yellowing of the leaves and affected brown vessels in the stems. Such plants then turn brown, begin to rot and die. As a preventative measure, tubers are treated with Ditan solution before planting.
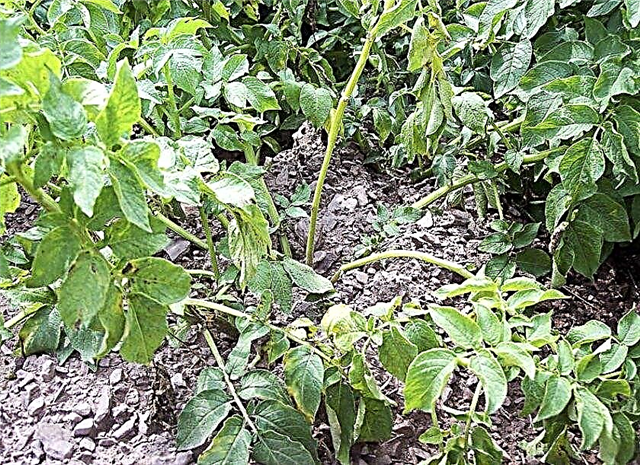

Viral diseases develop upon contact of sick and healthy plants. Viruses are carried by aphids and other pests, so the primary prevention of viruses is the fight against insect pests. And infected plants must be destroyed.
The main pests of potatoes:
- Colorado beetle - This is a large rounded insect with an orange-black striped chitinous cover. The beetle itself and its larvae feed on leaves. Manually collecting the pest is considered effective, since it is not too susceptible to insecticides.
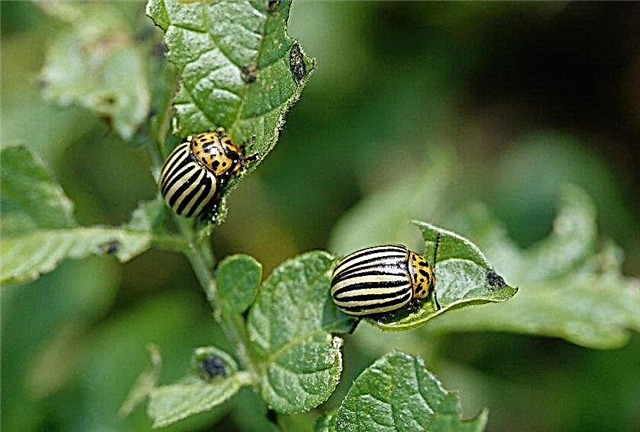

- Wireworms - are the larvae of the nutcracker beetle, which infect potato tubers. To protect against it, mustard is sown in the aisles. Its essential oils effectively ward off the insect from crops.

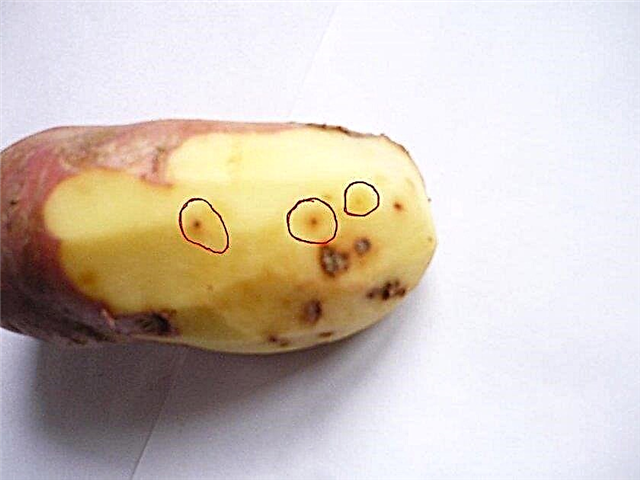
- Nematodes - microscopic whitish worms. They also damage tubers. To combat them, they use soil treatment with boiling water to a depth of not less than 20 cm. Tubers and soil are also treated with Karbofos.
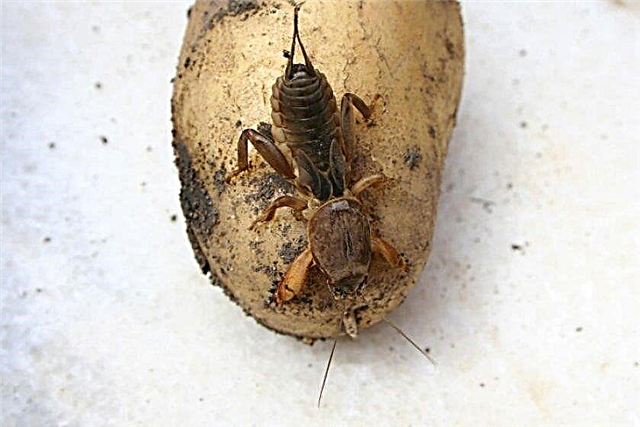
- Bears - large predatory insects that reach a length of 8 cm. Damage not only the tubers, but also the stems, as a result of which the plant dries up. Prestige, Corado, Biotlin and others are used against the bear.

- Caterpillars - these are the larvae of various butterflies, including potato scoops. They infect leaves as well as tubers. The Zolon preparation will help fight caterpillars.

To control insects, both chemical methods of control and environmentally friendly are used. Among them is the attraction of predatory insects and birds to the site. So, 1 ladybug in his life can destroy up to 5000 aphids. And you can attract it with odorous plants planted next to potatoes, for example, mustard. The choice of control methods often depends on the farmer's preferences.
Harvesting and storage
Barin's young potatoes are harvested on the 50th day after planting - by this time it is quite ready for consumption. But in order for it to fully mature, you need to wait another 20 days. The main sign of potato readiness is the withering of the tops. From this moment, count 2 weeks. During this time, the peel of the tubers will strengthen, which increases the shelf life.
Did you know? Potato and tomato — representatives of the same family. And this makes it possible to create their hybrids. So, the American breeder L. Burbank created a hybrid with potatoes at the bottom and tomatoes at the top of the plant. True, it was not possible to propagate such a plant.
If it rains and the tops do not dry out, it is permissible to raise the bushes with a shovel to break the contact of the roots with the ground. The tops will begin to fade in a couple of days. The weather on the day of digging should be dry and sunny. Digging from the edge of the bush to the center, so as not to damage the tubers.
After the potato is dug up, it is left to dry in a room with a temperature of +7 ... + 16 ° C for 2 weeks, and then placed in boxes. Tubers should be stored in a dry room at a temperature not exceeding + 10 ° С.

The Barin potato variety has good characteristics and is perfect for growing on personal plots. In addition, it is unpretentious, and if you apply simple rules for caring for it, it can show a high yield.




 Pour spring beds with Ridomil solution. This is a highly active fungicide that completely destroys pathogenic fungi both in the soil and on plants. It is important to remember that drugs of this class are used only for treatment, and not as a prophylactic. It will be better if you process the planting material with Zircon before planting. This drug protects the tubers from fungi, and also stimulates their growth and development. For potatoes, you need 20 drops per 1 liter of water. Against diseases of a fungal nature, crops are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux liquid (1%). It is advisable to do this even before you detect signs of the disease - before hilling.
Pour spring beds with Ridomil solution. This is a highly active fungicide that completely destroys pathogenic fungi both in the soil and on plants. It is important to remember that drugs of this class are used only for treatment, and not as a prophylactic. It will be better if you process the planting material with Zircon before planting. This drug protects the tubers from fungi, and also stimulates their growth and development. For potatoes, you need 20 drops per 1 liter of water. Against diseases of a fungal nature, crops are sprayed with a solution of Bordeaux liquid (1%). It is advisable to do this even before you detect signs of the disease - before hilling.



 It is detected at the stage of preparation of planting material. After 20 days, black pits appear on such tubers.
It is detected at the stage of preparation of planting material. After 20 days, black pits appear on such tubers.

















